Yikes: Meet the New Australian Dinosaur That Is Longer Than 2 Buses
Australotitan, or the “southern titan”, was a massive long-necked titanosaurian sauropod estimated to have reached 25–30 metres in length and 5–6.5m in height.
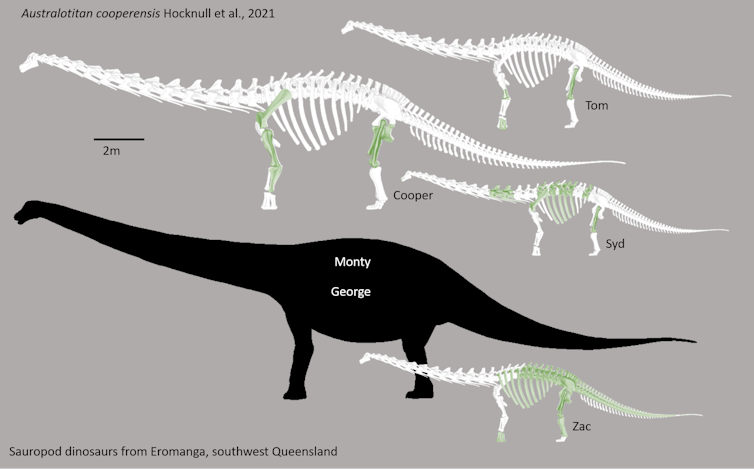
Today, a new Aussie dinosaur is being welcomed into the fold. Our study published in the journal PeerJ documents Australotitan cooperensis – Australia’s largest dinosaur species ever discovered, and the largest land-dwelling species to have walked the outback.
Australotitan, or the “southern titan”, was a massive long-necked titanosaurian sauropod estimated to have reached 25–30 metres in length and 5–6.5m in height. It weighed the equivalent of 1,400 red kangaroos.
It lived in southwest Queensland between 92–96 million years ago, when Australia was attached to Antarctica, and the last vestiges of a once-great inland sea had disappeared.
The discovery of Australotitan is a major new addition to the “terrible lizards” of Oz.
Like finding needles in haystack
Finding dinosaurs in Australia has been labelled an incredibly difficult task.
In outback Queensland, dinosaur sites are featureless plains. Compare that to many sites overseas, where mountain ranges, deep canyons or exposed badlands of heavily-eroded terrain can help reveal the ancient layers of preserved fossilised bones.

Today, the area where Australotitan lived is oil, gas and grazing country. Our study represents the first major step in documenting the dinosaurs from this fossil field.

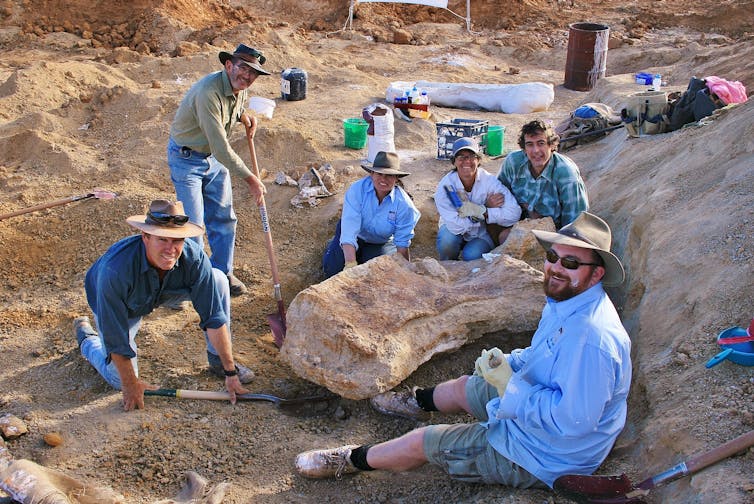
The first bones of Australotitan were excavated in 2006 and 2007 by Queensland Museum and Eromanga Natural History Museum palaeontologists and volunteers. We nicknamed this individual “Cooper” after the nearby freshwater lifeline, Cooper Creek.
After the excavation, we embarked on the long and painstaking removal of the rock that entombed Cooper’s bones. This was necessary for us to properly identify and compare each bone.

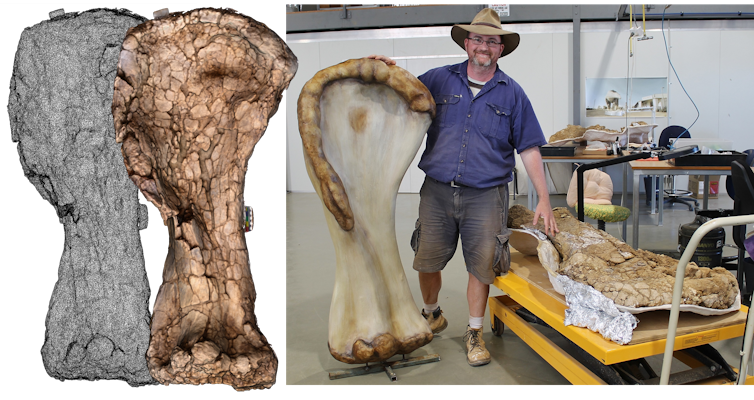
Thousands of kilograms bones in a backpack
We needed to compare Cooper’s bones to all other species of sauropod dinosaur known from both Australia and overseas, to confirm our suspicions of a new species.
But travelling from collection to collection at various museums to compare hundreds of kilograms of fragile dinosaur bones was simply not possible. So instead, we used 3D digital scanning technology which allowed us to virtually carry thousands of kilograms of dinosaur bones in one seven kilogram laptop.
These kinds of research projects have created a new opportunity for museums and researchers to share their amazing collections globally, with researchers and the public.

And thanks to two decades of effort by palaeontologists, citizen scientists, regional not-for-profit museums and local landowners, there has been a recent boom in Australian dinosaur discoveries.
We are family
Perhaps unsurprisingly, we found all four of the sauropod dinosaurs that lived in Australia between 96-92 million years ago (including Australotitan) were more closely related to one another than they were to other dinosaurs found elsewhere.
However, we couldn’t conclusively place any of these four related species together in the same place at the same time. This means they could have evolved through time to occupy very different habitats. It’s even possible they ever met.
The Aussie species share relations with titanosaurians from both South America and Asia, suggesting they dispersed from South America (via Antarctica) during periods of global warmth.
Or, they may have island-hopped across ancient island archipelagos, which would eventually make up the present-day terrains of Southeast Asia and the Philippines.
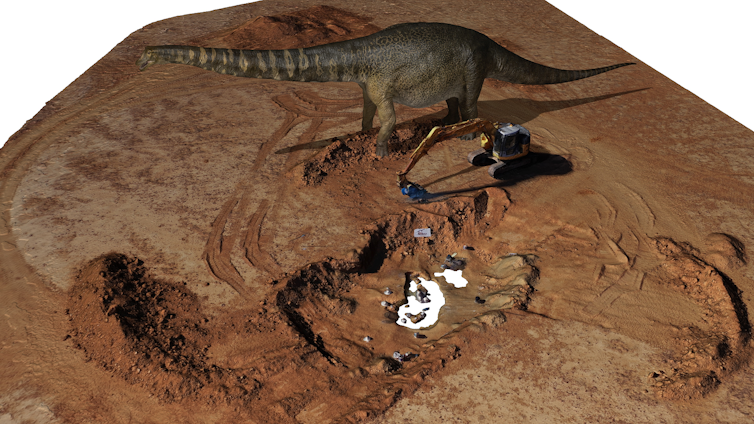
Trampling through the Cretaceous
Digitally capturing gigantic sauropod bones and fossil sites in 3D has led to some remarkable discoveries. Several of Cooper’s bones were found to be crushed by the footsteps of other sauropod dinosaurs.
What’s more, during Cooper’s excavation we uncovered another smaller sauropod skeleton — possibly a smaller Australotitan — trampled into a nearly 100m-long rock feature. We interpreted this to be a trample zone: an area of mud compressed under foot by massive sauropods as they moved along a pathway, or at the edge of a waterhole.
Similar trampling features can be seen today around Australian billabongs, or waterholes in Africa where the largest plant-eaters, such as elephants and hippopotamuses, trample mud into a hard layer.
In the case of the hippopotamus, they cut channels through the mud to navigate between precious water and food sources. Life in Australia during the Cretaceous period can be pictured similarly, except super-sized.
In the present, out there in Australia’s dinosaur country, you might find yourself staring across a barren plain imagining what other secrets this world of long-lost giants will reveal.
Scott Hocknull, Senior Curator of Geosciences, Queensland Museum, and Honorary Research Fellow, The University of Melbourne
Róchelle Lawrence, Senior Research Assistant (Palaeontology), Queensland Museum
This article first appeared at The Conversation and is being republished via a Creative Commons license.
Image: Reuters.

